简介
本章主要覆盖以下几方面,单元测试,EmbeddedChannel的简介,使用EmbeddedChannel测试ChannelHandlers
ChannelHandlers是netty应用模块中最重要的一部分,因此彻底的测试在开发过程中也是标准的一部分,很多最好的事件表名你的测试并不能证明你的实现是正确的,但是使用Unit Testing 总是很容易隔离问题。
EmbeddedChannel 概述
Netty中提供了一个叫做embedded transport 为了测试ChannelHandlers,这个具有传输特性的channel实现,EmbeddedChannel,提供一种简单的方式让事件通过整个Pipeline
这种注意是很直接的,你可以用EmbeddedChannel写入站与出站的数据,然后检测通过ChannelPipeline的数据是否符合预期

以下为具体的流程图
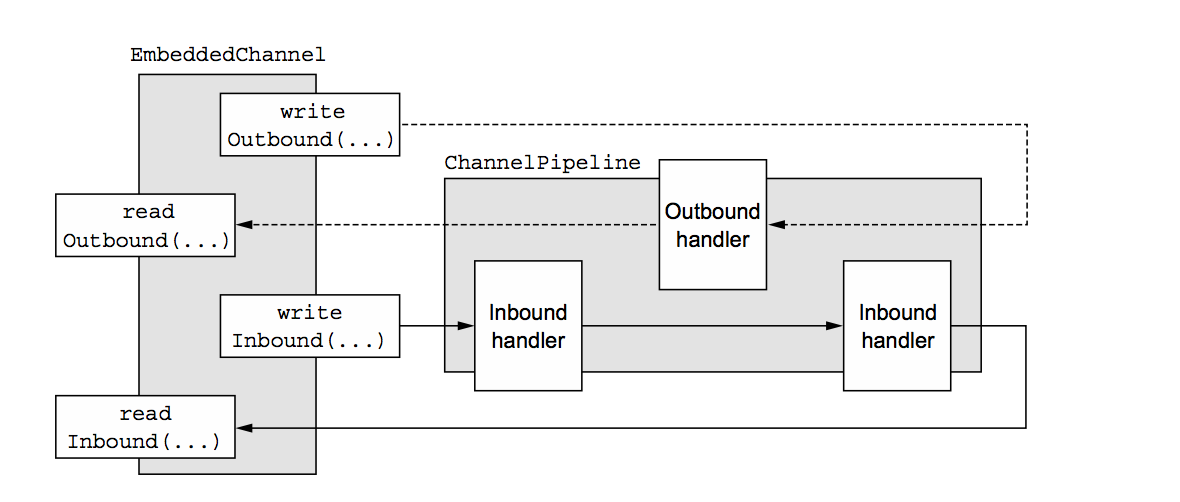
入站数据由ChannelInboundHandlers 处理并且表达数据是从远端处理,出站数据是由ChannelOutboundHandlers 并且表示数据是由远端写的,取决于你所需要测试的channleHandler
使用EmbeddedChannel测试ChannelHandlers
测试入站数据
以下为表示了一个简单的ByteToMessageDecoder的实现,给与充足的数据,它将提供一个固定的大小,如果没有足够的数据去读,它将会等待下个数据块并且再次检查是否有一个固定大小的对象生成
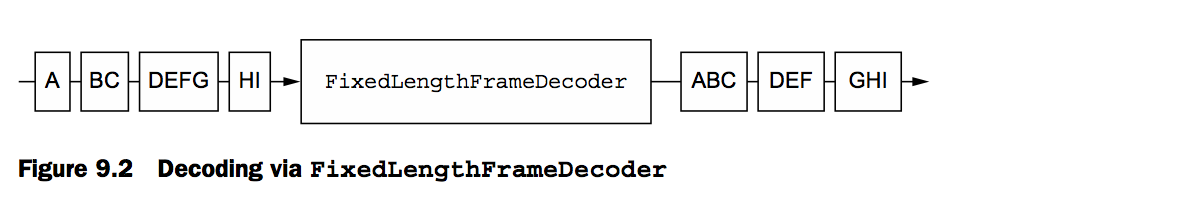
你可以看到上面这张图右边的部分,特别是解码生产一个固定大小的对象,因此它可能需要超过一个时间提供足够的字节生产对象。最终每一个对象都将通过下一个ChannelHandler直至通过整个链条
1 | public class FixedLengthFrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder { |
以下为测试代码
1 | public class FixedLengthFrameDecoderTest { |
测试出站数据
以下主要以一个MessageToMessage的编码器为例,将负整数转换为整整数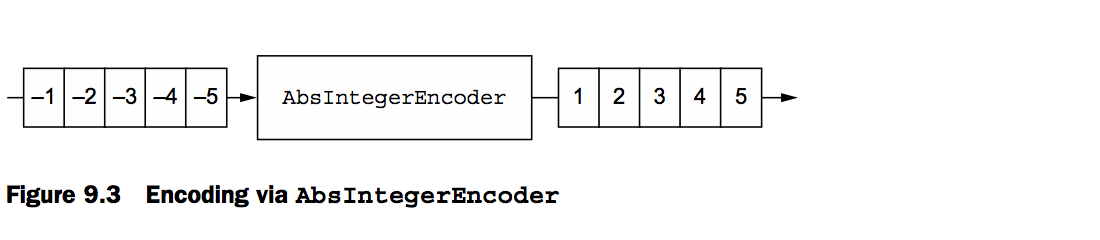
1 | public class AbsIntegerEncoder extends |
1.写负整数(四个字节的数据到ByteBuf)
2.创建一个EmbeddedChannel并且分配了一个Encoder
3.调用writeOutbound 写入数据ByteBuf
4.标记channel已经写入完成
5.读取所有的出站数据并且确认是否已经转换为正整数
1 | public class AbsIntegerEncoderTest { |
测试异常处理
主要测试当入站数据的大小超过指定长度,会抛出异常
1 | public class FrameChunkDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder { |
测试
1 | public class FrameChunkDecoderTest { |
这部分主要使用try…catch来测试是否有异常被抛出,因为这个是运行时异常,这个很容易测试是否一个异常在处理数据的过程中被捕捉并且处理的。
总结
以一个侵入少的例如JUnit单元测试是一个极度有效的方式保证代码的正确性并且增强可维护性。在这章,你可以学到netty提供的工具怎么测试您自己的ChannelHandler
在下一章您将聚焦于怎么用netty写一个真实的应用。我们将不会表示更多的测试用例,希望你自己保持思考我们想表达的测试方法的重要性。

