本章主要覆盖以下方面
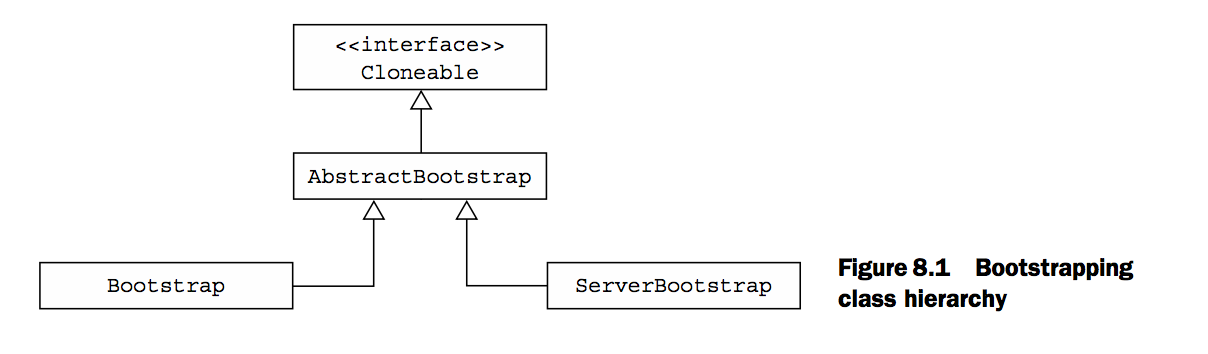
Bootstrap 类
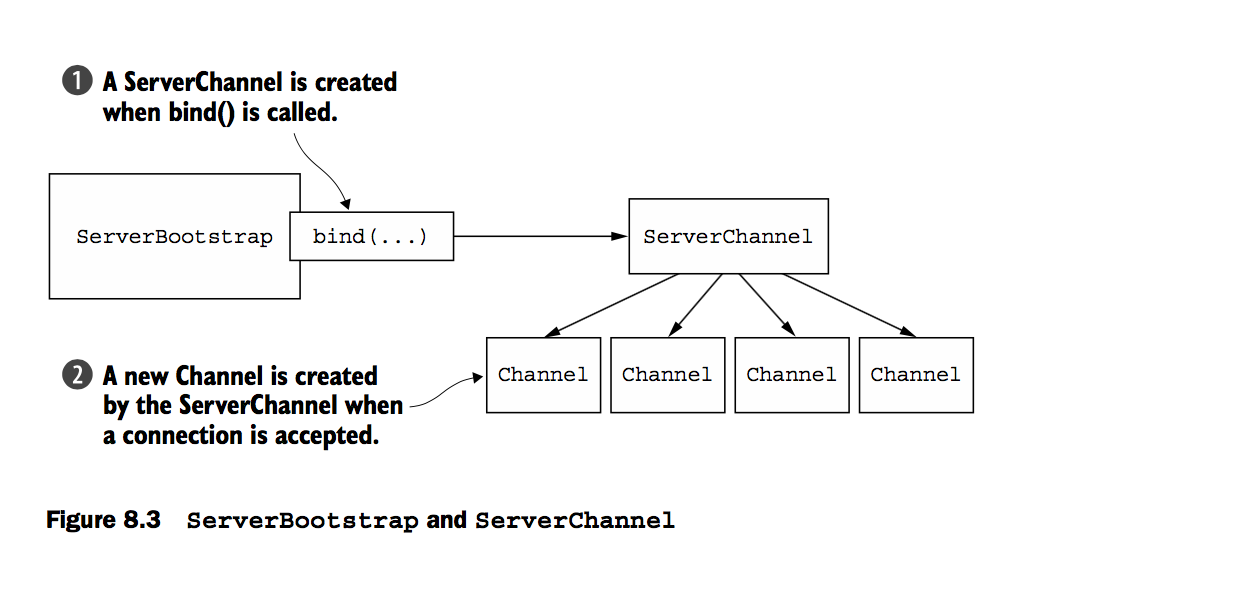
一个server端的Bootstrap,如上图所示,主要用于接收连接,并且创建一个子Channels与客户端服务,然而客户端只需要一个,因此不需要父级的channel。对于udp的服务端也一样如此
1 | public abstract class AbstractBootstrap |
Bootstraping 客户端以及无连接协议
以下是Bootstraping的API
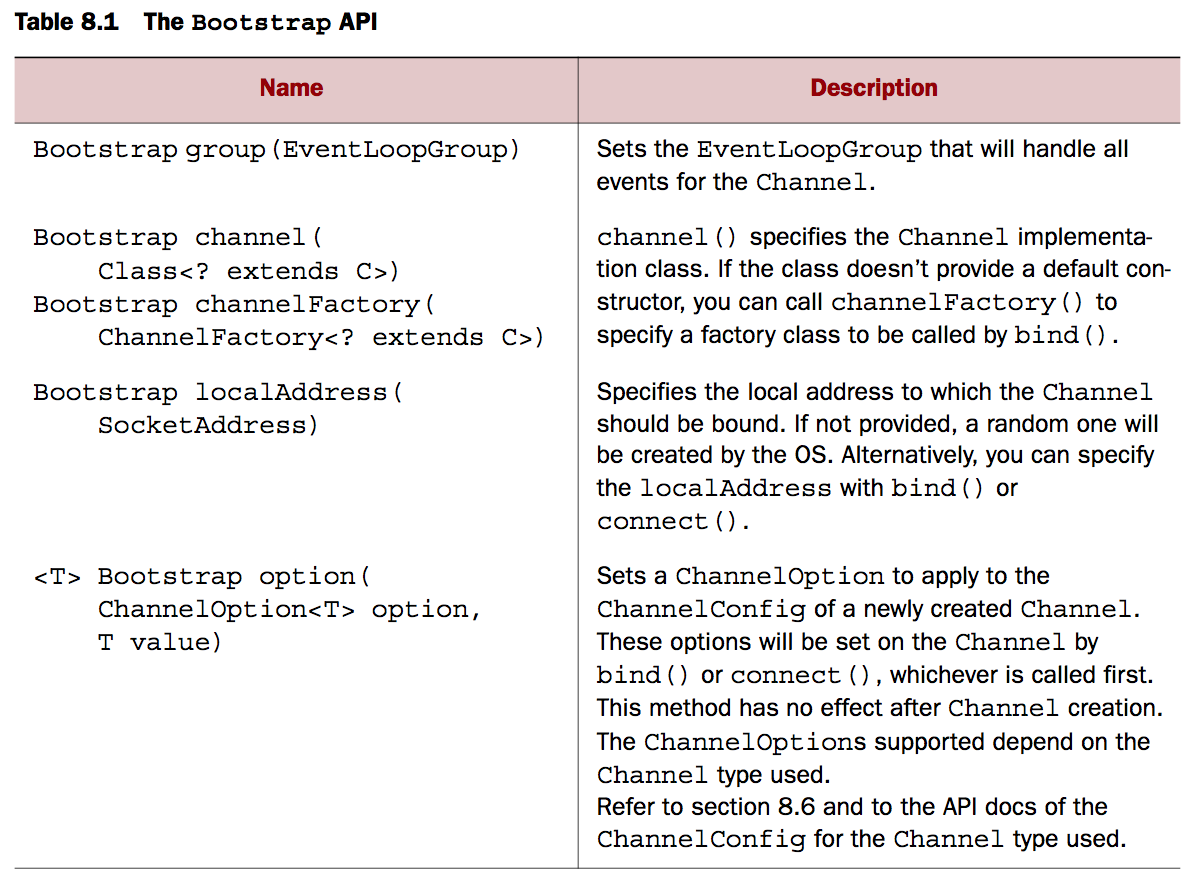
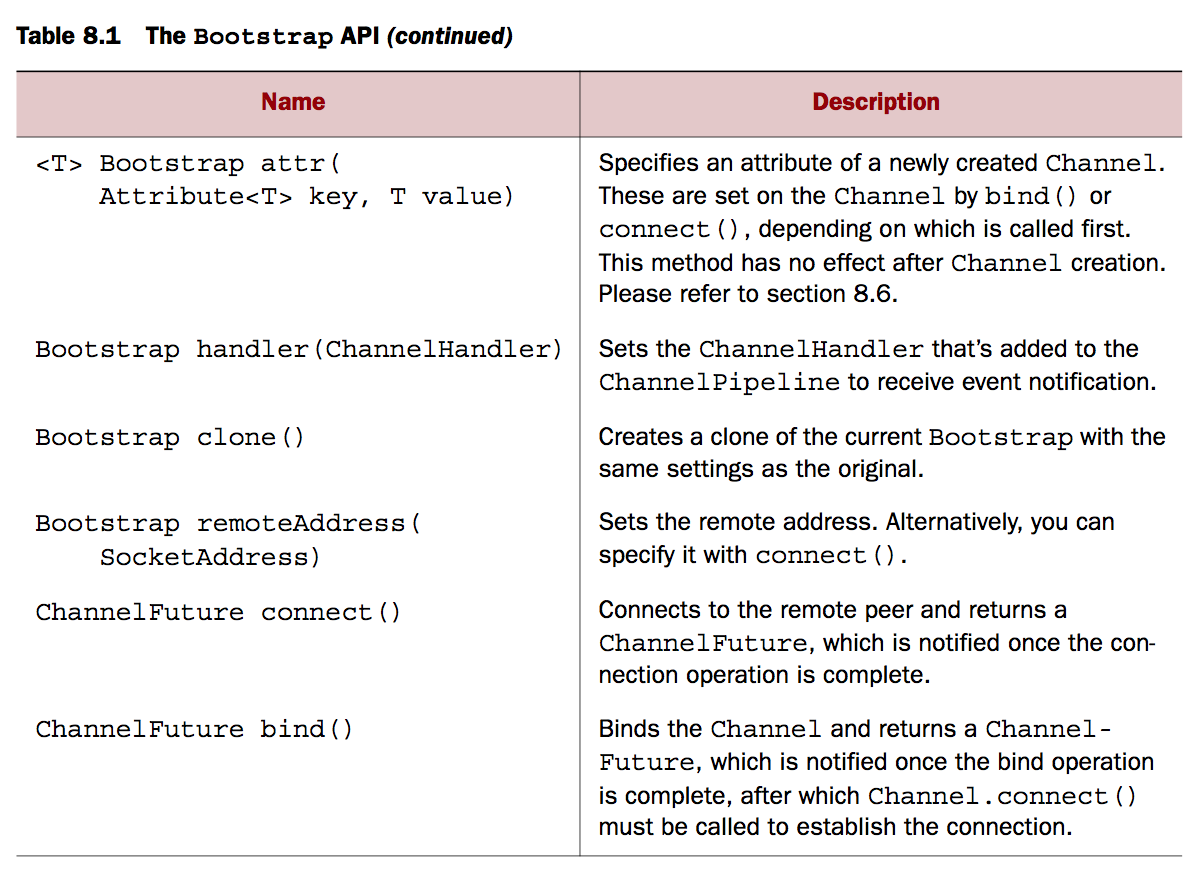
引导客户端
Bootstrap 类主要负责为客户端创建channels以及为应用指定连接协议
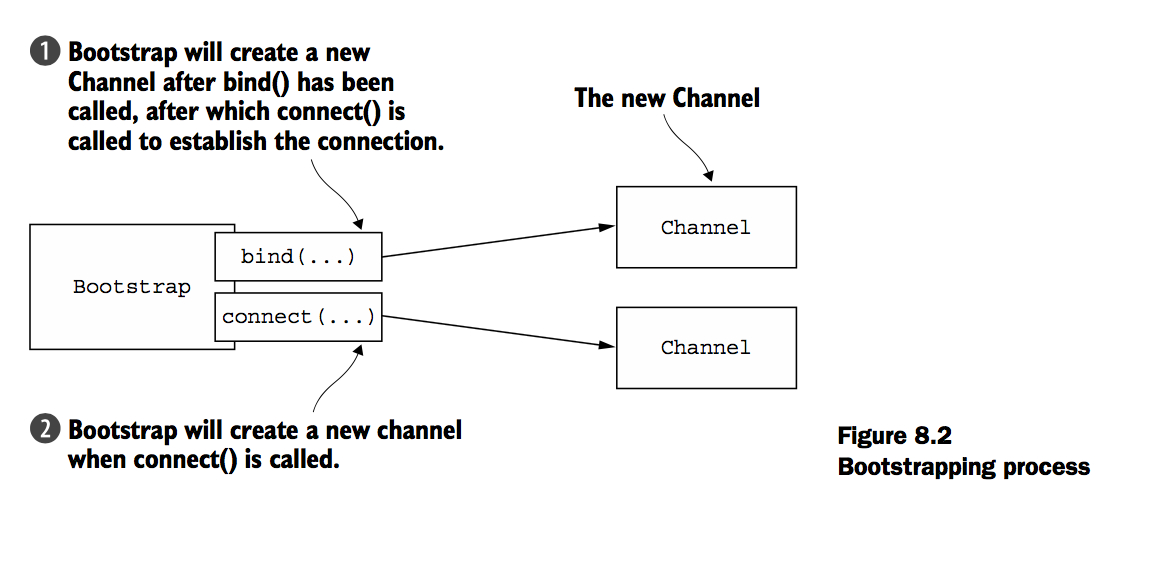
例如以下为使用NIO TCP连接
1 | EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); |
Channel 与 EventLoopGroup 组合
channel与EventLoopGroup要对应起来,是NIO的channel就要对应NIo的EventLoopGroup
当Bootstrap bind() 或者 connect() 的时候,一定要先设置以下三项
- group()
- channel() 或者 channelFactory()
- handler
Bootstrapping 服务端
这一节主要讲述Bootstrapping 服务端的相关APi以及使用用例

####
你可以发现服务端的Bootstrapping与客户端存在差别,例如childHandler,childAttr以及childOption,以上这些操作传统的server应用都有,特别是ServerChannel要实现创建相关的子channel,主要用于已经接入的连接。所以ServerChannel管理一些数量的子channel
下图为例:
1 | NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); |
从channle中引导客户端
如果你的程序既有服务,又有客户端场景,因此我们可能需要创建Bootstrap的客户端,由此连接到远程peer,但是这个是最没有效率的解决方法,这种方法可能需要你定义另一个EventLoop,这样就会产生额外的线程,以及上下文切换。
一个更好的方法是共享已经介入的channel的EventLoop,通过Bootstrap的group方法,因为所有的channles斗湖被分配到一个EventLoop使用同样的线程,这避免了额外的线程创建。
如下图所示: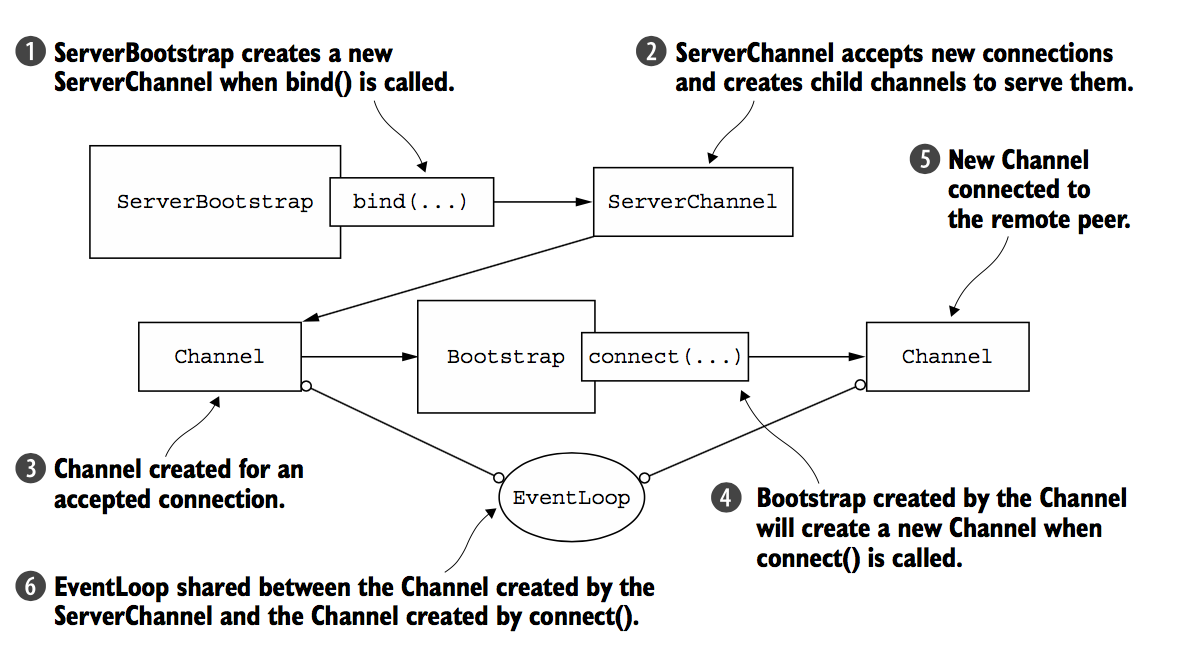
1 | public class BootstrapSharingEventLoopGroup { |
主要是无论什么时候都要考虑重用EventLoop
在一个bootstrap中添加多个ChannelHandler
上文所示主要是使用handler与childHandler中只能绑定一个ChannelHandler,如何绑定多个呢?
答案是使用netty提供的一个ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter 的子类ChannelInitializer这个类1
2
3
4
5
6public abstract class ChannelInitializer<C extends Channel>
extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter
//使用这个方法
protected abstract void initChannel(C ch) throws Exception;
当有channle绑定到EvnetLoop的时候,这个initChannel方法就会调用,然后在方法完成后,会将自己从ChannelPipeline中去除
1 | public class BootstrapWithInitializer { |
使用netty 的ChannelOptions以及attributes
手动配置每个channel是单调乏味的。我们可以使用option()方法对Bootstrap配置ChannelOptions,ChannelOptions提供了相关keep-alive、timeout以及buffer的设置等。
1 | public class BootstrapClientWithOptionsAndAttrs { |
引导一个UDP的channels DatagramChannels
前面的channel例子都是基于Tcp的,但是netty也提供了UDP的实现,区别主要在于connnect以及bind
···
public void bootstrap() {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(new OioEventLoopGroup()).channel(
OioDatagramChannel.class).handler(
new SimpleChannelInboundHandler
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
DatagramPacket msg) throws Exception {
// Do something with the packet
}
}
);
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(0));
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture)
throws Exception {
if (channelFuture.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println(“Channel bound”);
} else {
System.err.println(“Bind attempt failed”);
channelFuture.cause().printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
···
关闭
如何优雅的关闭
1 | EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); |
不建议:可选的,你可以使用channel.close() 确定关闭所有活跃的channel,然后再关闭EventLoop。
但是在所有的例子中,记住先关闭EventLoop

